Mark To Market What It Is And How It Works: All You Need To Know

For instance, companies generally decide to mark the value of their positions to the market at the end of each trading day. For instance, the closing ask price at the end of the day mark to market accounting will be used for valuation. Gains and losses in mark-to-marketing accounting are calculated based on fluctuations, whether day by day or over time.
- The concept is fundamental for ensuring that financial statements reflect the most recent market conditions.
- It’s the primary accounting method for financial services and investment companies where the assets’ price needs to be adjusted daily.
- Mark to market aims to provide a realistic appraisal of an institution’s or company’s current financial situation based on current market conditions.
- Moreover, despite these risks, investing in the stock market can be a lucrative way to grow your wealth.
- The end effect of the Enron scandal was to bring into question the accounting practices of many financial institutions.
- Remember that fair market value is based on what two willing parties to a transaction would agree upon in regards to the sale of the asset in question.
The Importance of Mark to Market in Finance
Mark to market accounting, often called fair value accounting, translates market prices into financial statements to present a real-time view of assets and liabilities. Mark to market increases transparency for stakeholders, but it also amplifies income statement volatility and raises governance demands that auditors and consultancies—Deloitte, PwC and KPMG among them—must address. In investing, mark-to-market (MTM) refers to the practice of valuing investments at their current market prices or fair values, rather than their original purchase prices or historical costs. This approach allows investors to assess the performance of their investments in real-time and make informed decisions based on current market conditions. Mark-to-market accounting is particularly relevant for investors who actively trade securities or hold assets that are subject to market fluctuations.
How Mark to market Works

Companies that follow generally accepted accounting principles must use the historical cost method for certain assets. More specifically, this accounting method is required to be used when reporting fixed assets. It cultivates a truer valuation that can protect and inform investors, providing a real-time financial map, which is crucial for making informed decisions. It also aligns accounting practices with today’s fast-moving markets, so companies using MTM are less likely to find themselves with vastly outdated valuations.
Steps to Calculate Mark to Market in Futures
Let’s say Sam has $50,000 in their trading account and wants to buy one contract. But this isn’t always the case when it comes to small cap stocks with low liquidity. Futures contracts are leveraged instruments that allow a trader to hold a long or short position several times larger than the amount (margin) they initially commit to a trade. The ratio between the initial margin and the exposure of a trade is the leverage. There’s also usually a multiplier used to calculate the value of one contract. Placing a value on a private company is a subjective process and the estimate will vary depending on who you ask.
- Appreciate offers real-time market value tracking and precise MTM reporting to tackle these.
- In the context of futures trading, MTM helps ensure that unrealized gains and losses are quickly and accurately reflected on a daily basis.
- This means they need to be fungible – meaning one unit is the same as another unit.
- Passionate about simplifying money matters, he crafts clear, engaging content on personal finance to help readers make informed financial decisions.
- Returning to the same catering company from earlier, say they went to a lender seeking a $5 million loan to open a larger food processing plant to expand into prepackaged frozen meals.
- Access daily AI-powered content with highlights from our industry-leading research, reports and market data to help you make more informed decisions.
Mark to Market in Personal Accounting
In futures trading, marking to market (MTM) is the daily retained earnings valuation of open futures contracts to reflect their current market value. This process ensures that traders maintain sufficient margin to cover potential losses. It’s a method that utilizes fair value accounting, offering everyone a transparent look at a company’s or individual’s financial health by reflecting the true worth of their assets and liabilities at any given moment. This mark-to-market system means that financial statements are always showing a picture in real-time, aligning values with the ebbs and flows of the market, as outlined in FAS 157, Fair Value Measurements. Mark to market (MTM) is a method of measuring the fair value of accounts that can fluctuate over time, such as assets and liabilities. Mark to market aims to provide a realistic appraisal of an institution’s or company’s current financial situation based on current market conditions.
- This practice helps recognise gains and losses promptly and maintains accurate margin requirements.
- Under IRC Sec 475(f), MTM is for a person who is engaged in a trade or business as a trader in securities who elects …
- The mark-to-market accounting principle involves adjusting the value of an asset to reflect the current market conditions.
- Mark to market will adjust the value of assets held on a balance sheet or in an account based on the current market value of those assets.
- Industries such as banking, investment, and trading commonly use mark-to-market accounting to reflect the real-time value of financial instruments and investments.
In investments, mark-to-market accounting involves adjusting the value of securities to their current market price at each reporting period. This provides a more accurate picture of an investment’s value but can introduce volatility. Mark-to-market involves adjusting the value of an asset or liability to reflect its fair market value at a specific point in time. This bookkeeping and payroll services means periodically updating the value based on current market conditions rather than relying on the original purchase price. It’s the primary accounting method for financial services and investment companies where the assets’ price needs to be adjusted daily.
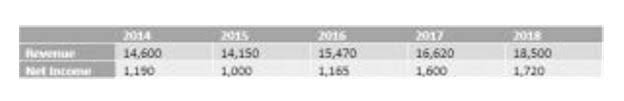
Risks of MTM
Gain hands-on experience with Excel-based financial modeling, real-world case studies, and downloadable templates. Upon completion, earn a recognized certificate to enhance your career prospects in finance and investment. It is commonly applied to liquid securities with readily available market prices like stocks and bonds. But other assets like fixed assets, intangibles, or advances may be excluded from MTM requirements, as estimating fair value can be difficult or yield counterintuitive results in such cases. Mark to Market accounting is an indispensable yet complicated feature of modern financial reporting.

Six months later when Jim sells the shares, they are trading at $500, so that means he has lost $10,000. The broker still has the $5,000 margin, but if Jim is unable to pay the remaining $5,000, the broker will be out of pocket. Discover how to reduce taxable income with smart financial strategies that can help mitigate the impact of MTM losses. For businesses, this approach may highlight areas where tax planning strategies are essential, especially when dealing with volatile markets. Let us understand the concept mark to market accounting treatment with the help of a suitable example.
These types of assets typically include company land or equipment that has depreciated over the course of its useful life, including assets such as buildings and machinery. Investors typically buy and sell securities and expect income from dividends, interest, or capital appreciation. They buy and sell these securities and hold them for personal investment; they’re not conducting a trade or business. Most investors are individuals and hold these securities for a substantial period of time.



